Controlled Environment Agriculture – The Future of Farming
In a world facing escalating challenges such as climate change, urbanization, and a growing population, traditional farming methods are increasingly under pressure.
Enter Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) – a transformative approach to food production that offers an efficient solution to modern agricultural woes.
In short, Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) is a technology-driven method of food production that uses both outdoor structures and indoor systems. Let us dive into it:
What is Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA)?
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) is an advanced and intensive form of hydroponic or aeroponic agriculture where plants are grown within a controlled environment to optimize growth conditions. This can include greenhouses, vertical farms, and even fully enclosed indoor farms.
The key components of CEA include precise control over temperature, humidity, light, and nutrients, which allows for year-round production regardless of external weather conditions.
Why is CEA so interesting?
A resilient food system must include all scales and types of agriculture. With climate change threatening traditional farming and consumers seeking unique products, Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) can play a crucial role in ensuring a robust and nutritious global food supply.
CEA can produce high-quality food close to consumers while using minimal water and other resources. Many of the fresh tomatoes, herbs, and leafy greens we enjoy are already grown in controlled environments, such as shade structures and greenhouses. Additionally, greens grown entirely under artificial lights in enclosed indoor systems are becoming more common in the market.
Looking ahead, CEA is likely to become a key complement to traditional outdoor farming methods. CEA can reduce the need for water, nutrients, and chemicals, lower the risk of foodborne pathogens, and save on labor costs. Moreover, CEA systems can be located in urban areas unsuitable for conventional agriculture, bringing food production closer to consumers and utilizing existing space efficiently.

Types of Controlled Environment Agriculture Practices
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) include several innovative farming methods, each designed to optimize growing conditions and maximize resource efficiency. Here are the main types of CEA:
- Greenhouses: Greenhouses provide a controlled environment with regulated temperature, humidity, and light. They protect crops from extreme weather and pests, extending the growing season and improving yield quality. Greenhouses can employ various CEA methods like hydroponics or traditional soil-based growing.
- Hydroponics: This method involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water solutions without soil. Hydroponic systems can be designed to use less water and allow for faster plant growth.
- Aeroponics: In aeroponics, plants are grown in an air or mist environment without the use of soil or an aggregate medium. Nutrients are delivered via a mist, which can improve nutrient uptake and efficiency.
- Aquaponics: Combining aquaculture (raising fish) with hydroponics, aquaponics creates a symbiotic environment where fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, and the plants help filter and clean the water for the fish.
- Vertical Farming: Vertical farming stacks layers of crops in a controlled environment, making it possible to grow more food in less space. This approach is particularly effective in urban areas where land is limited.

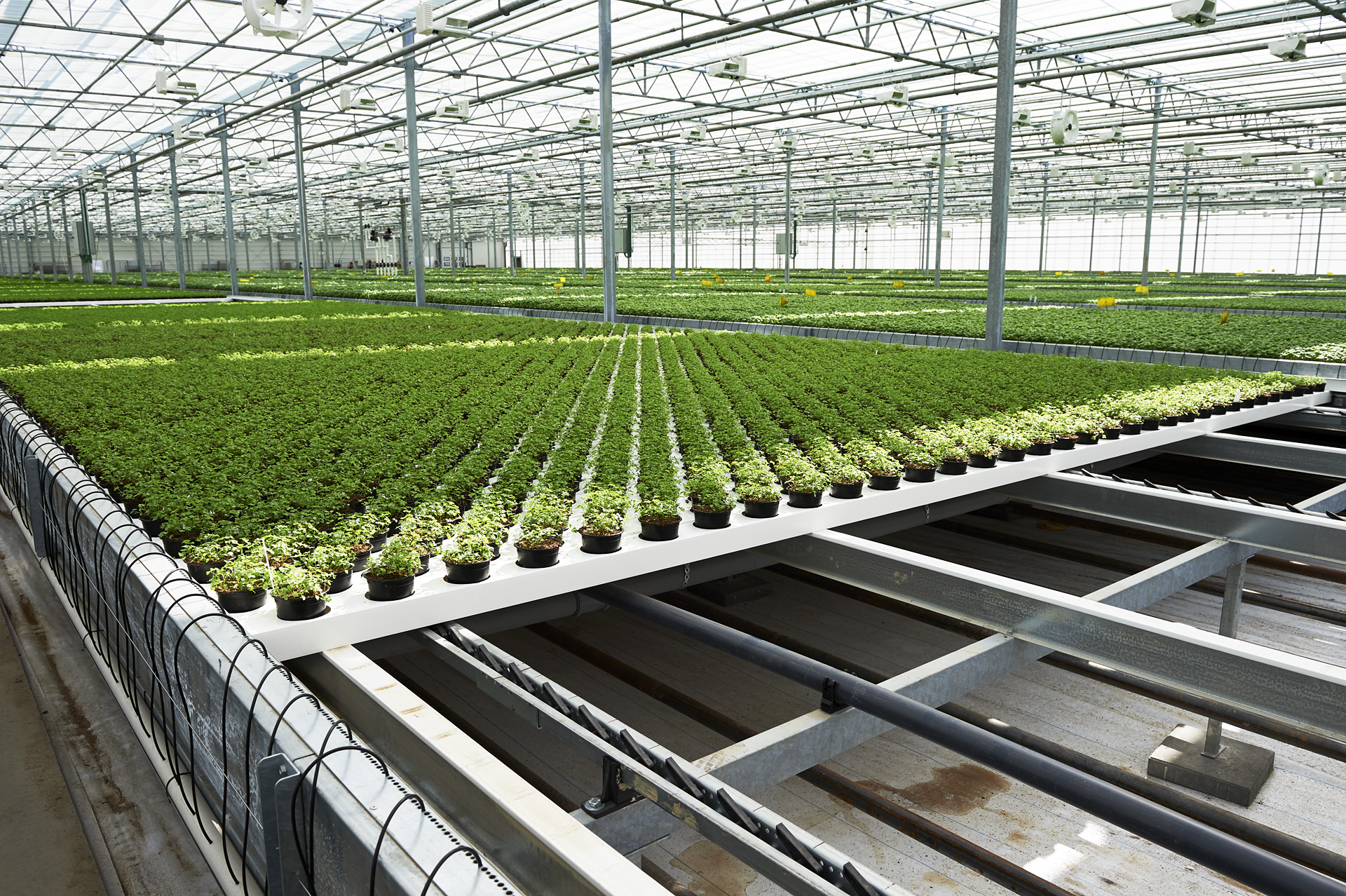
What are the Benefits of Controlled Environment Agriculture?
Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) offers a wide range of benefits, making it an attractive and efficient solution for modern food production. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Ressource Efficiency: CEA systems use resources more efficiently than traditional farming methods. They can significantly reduce water usage, often by up to 90% compared to soil-based agriculture, through methods like hydroponics and aeroponics. Additionally, CEA optimizes space utilization, allowing for higher crop yields per square meter of land.
- Climate Resilience: CEA provides a controlled environment that is less susceptible to the effects of climate change. By regulating factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, CEA systems can mitigate the impact of extreme weather events and ensure consistent crop production year-round.
- Higher Quality and Yields: CEA allows for precise control over growing conditions, resulting in consistent and often higher yields compared to traditional farming. Moreover, CEA-grown crops are typically of high quality, with improved taste, texture, and nutritional content.
- Year-Round Production: CEA enables year-round production regardless of external weather conditions. By providing a stable growing environment, CEA systems can ensure a continuous and reliable food supply, reducing dependence on seasonal harvests.
- Urban Agriculture: CEA systems can be implemented in urban areas where space is limited, bringing food production closer to consumers. By utilizing rooftops, vacant lots, or even repurposed buildings, urban CEA contributes to food security, community resilience, and economic development in cities.
Challenges and Considerations of CEA
While CEA offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. The initial setup cost for CEA systems can be high, and they require significant technical expertise to manage effectively.
Energy consumption can also be a concern, especially in indoor farms that rely heavily on artificial lighting. However, advancements in renewable energy and energy-efficient technologies are helping to mitigate these issues.
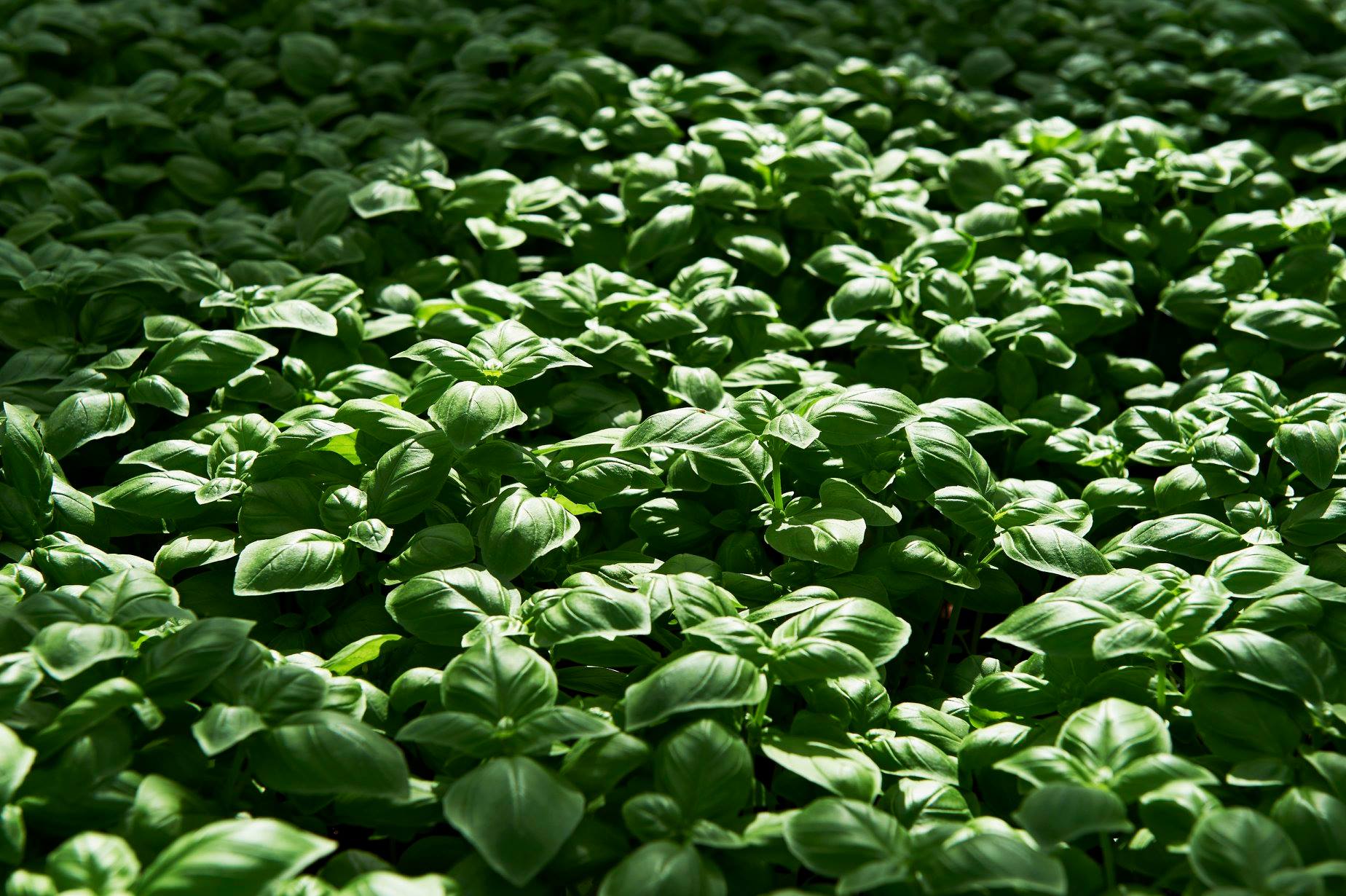

Moving Gutter Systems as a good practice of CEA
Our Moving Gutter Systems can help overcome these challenges as it is a superior choice in CEA. For instance, it provides optimal nutrient distribution by precisely controlling the water and nutrients each plant receives, ensuring uniform growth and maximizing crop yields.
By preventing stagnant water, it minimizes the risk of root diseases and reduces the need for chemical interventions. The efficient recycling of water and nutrients in our system reduces waste and promotes general efficiency in Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA) operations.
In summary, our Moving Gutter System offers several advantages in CEA, including optimal nutrient distribution, enhanced root aeration, prevention of root diseases, efficient water and nutrient recycling, improved temperature regulation, and increased oxygenation. By incorporating our system into CEA operations, growers can achieve higher yields, better crop quality, and increased sustainability.