Navigating Vertical Farming: Overcoming Challenges and Implementing Solutions
In recent years, the agricultural sector has experienced a transformative shift, driven by the need to address global challenges such as population growth, climate change, and resource scarcity. Among the various innovative techniques emerging in response to these challenges, Vertical Farming has gained significant attention as a revolutionary approach to food production.
This article takes a closer look at Vertical Farming, exploring the challenges it faces, such as high initial costs and energy demands, as well as the many benefits it offers, including year-round crop production, improved sustainability, and the potential to bring farming closer to urban centers.
What is Vertical Farming?
Vertical Farming Systems has revolutionized plant cultivation by employing vertically stacked layers or structures. This innovative approach utilizes cutting-edge technologies like hydroponics, which grows plants without soil, aeroponics, which suspends plants in the air and mists their roots with nutrients, and artificial lighting to simulate ideal growth conditions for plants.
By embracing these advanced techniques, Vertical Farming creates controlled environments where factors such as light, temperature, and humidity are meticulously regulated to optimize plant growth. This precision allows crops to thrive more efficiently compared to traditional soil-based farming methods.
Furthermore, Vertical Farming maximizes the efficient use of space by stacking crops vertically, thereby significantly expanding the available growing area within a limited footprint. This spatial efficiency is particularly advantageous in urban environments where arable land is scarce.
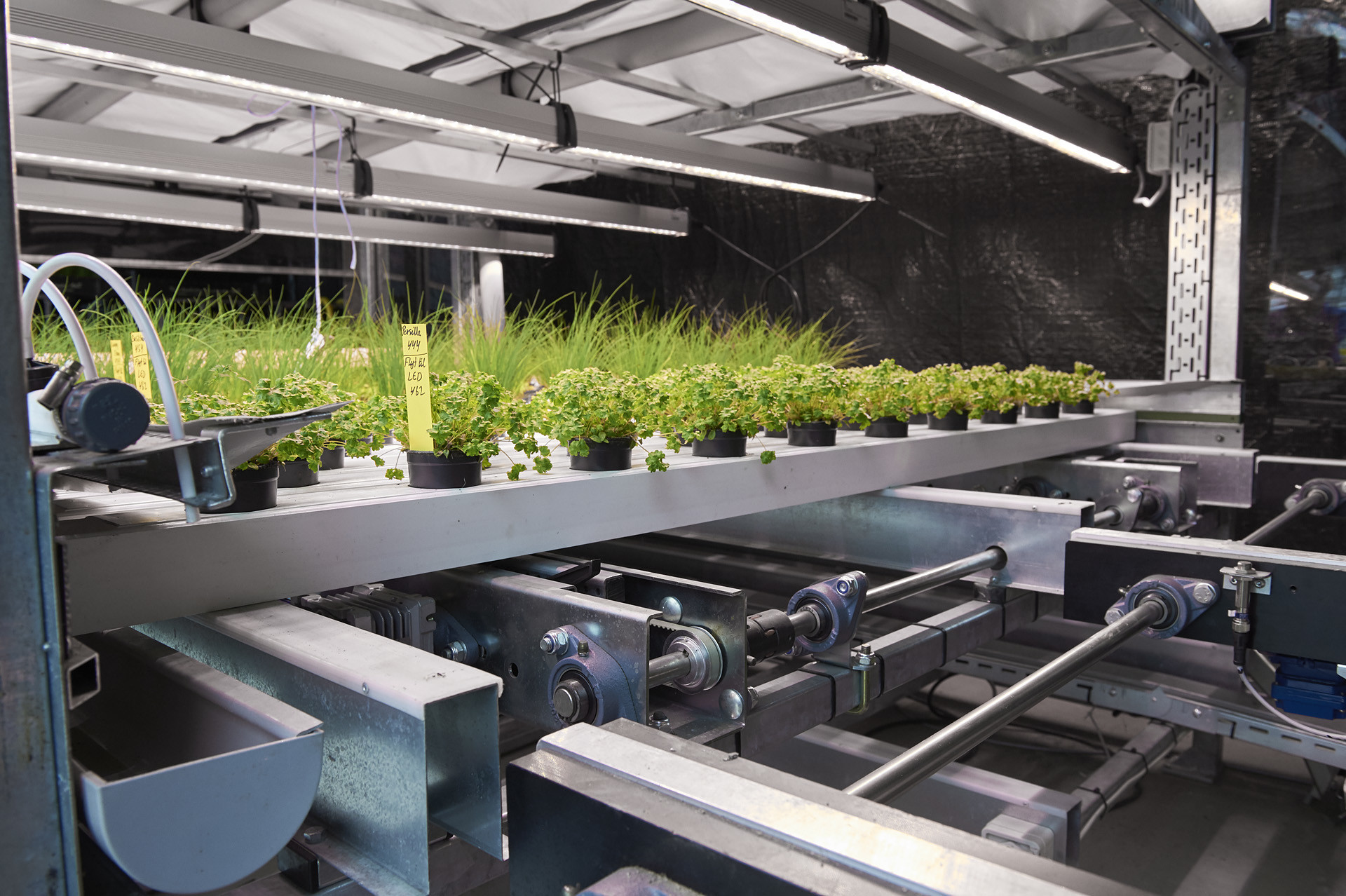

Challenges of Vertical Farming
Starting a Vertical Farm requires a large initial investment in infrastructure, technology, and specialized equipment. The costs of setting up and maintaining systems like hydroponics or aeroponics can be high. However, as technology improves and the industry grows, these costs are expected to decrease over time.
Vertical Farming works best for growing crops like leafy greens and herbs, but it can be challenging for crops that need more space. This creates concerns about genetic diversity and the long-term sustainability of growing certain crops in Vertical Farms.
One of the main challenges of Vertical Farming is that it relies on artificial lighting for photosynthesis, which leads to high energy use. This increases operational costs and has an environmental impact. However, advances in LED lighting and renewable energy sources are helping to reduce energy consumption.
Running a Vertical Farm also requires specialized knowledge in plant biology, engineering, and data analytics. Finding and keeping skilled workers in regions where Vertical Farming is still new can be a challenge.
Solutions to Vertical Farming
Despite the challenges of Vertical Farming, it offers many solutions. For example, Vertical Farming significantly increases crop yields compared to traditional farming methods. By growing plants in layers and controlling environmental factors like light, temperature, and humidity, it boosts productivity.
Vertical Farming also helps solve the problem of limited farmland due to population growth. It uses unused urban spaces for farming, making the most of small areas and increasing food production in crowded cities.
Another solution to the challenges of Vertical Farming is the use of hydroponics, which saves up to 90% more water than traditional farming. This makes farming more sustainable and reduces waste. Additionally, Vertical Farms create controlled environments, so they are not affected by seasonal changes or bad weather, ensuring a reliable food supply, especially in areas with harsh climates.
Finally, Vertical Farms are often located near cities, which means fresh produce can be delivered quickly to consumers. This cuts down on transportation costs, ensures high-quality local produce, and helps reduce carbon emissions in the food supply chain.
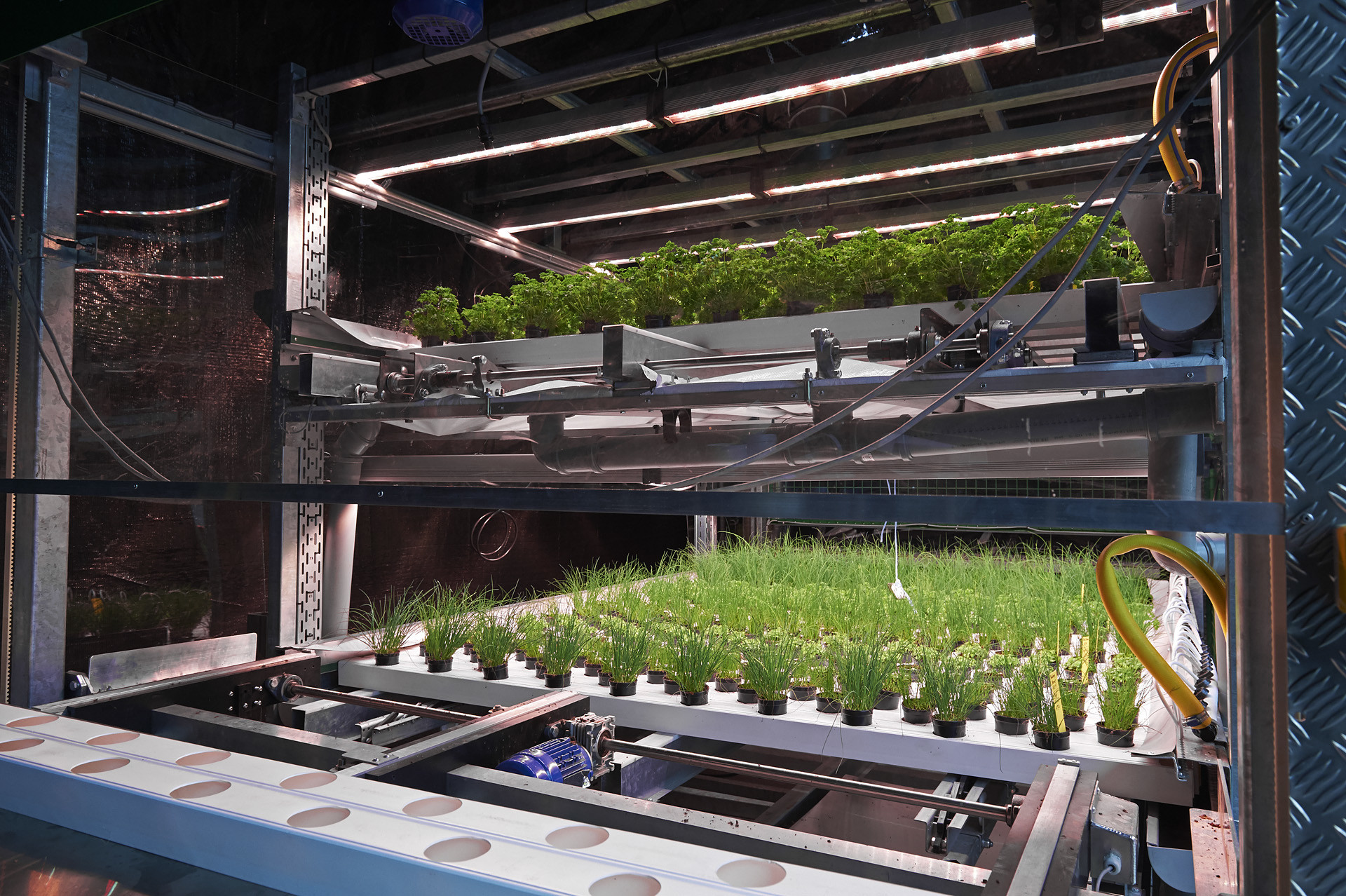

What does the Future hold for Vertical Farming?
The future of Vertical Farming looks very promising, with the potential to transform the agriculture industry. As technology improves, farming methods become more efficient, and costs go down, Vertical Farming will become more affordable and widely available. However, it’s important to consider both the challenges and solutions in vertical farming to make the most of its potential.
As more people recognize the environmental and social benefits of Vertical Farming, it’s likely to play a big role in sustainable food production worldwide. This method offers a way to tackle issues like land shortage, water use, and climate change, helping meet the food needs of a growing population.
With ongoing research, cooperation, and investment, Vertical Farming can reshape agriculture, overcoming challenges like high energy costs and upfront expenses to ensure a secure and sustainable food supply for the future.
How does Viemose DGS provide Solutions to the Challenges of Vertical Farming?
At Viemose DGS, we combine the benefits of Vertical and Horizontal Farming. By using our Moving Gutter System in a stacked setup, we have improved traditional indoor farming methods, tackling many of the challenges in vertical farming.
Our system is fully automated, which reduces the need for labor, energy, and water. We use the Nutrient Film Technique, allowing us to grow healthy crops year-round.
Our systems can be set up in various locations, like old warehouses, basements, or existing buildings. This makes it easier to grow crops closer to markets, reducing transportation distances and ensuring fresh produce.