Vertical Agriculture: Everything you need to know
With the world’s population steadily increasing, traditional farming methods are facing unprecedented challenges. These methods not only strain our environment but also struggle to meet the growing demand for food. In response to these issues, Vertical Agriculture has emerged as a promising solution.
In the past 40 years, we have lost a third of our usable farmland. To ensure we can feed future generations, we need to adopt new, sustainable farming methods.
In this article we will explore what Vertical Agriculture is and how it works, showing how it can help us produce more food while protecting the planet.
What is Vertical Agriculture?
Vertical Agriculture involves cultivating crops on vertical surfaces instead of traditional horizontal fields. This approach allows farmers to grow significantly more food using the same or even less land.
These vertical layers can be integrated into buildings like skyscrapers, warehouses, shipping containers, and greenhouses, utilizing otherwise non-arable spaces.
However, Vertical Farming requires precise control over temperature, light, water, and humidity. Without maintaining this delicate balance, entire crops can be lost, similar to how traditional farms suffer during droughts or floods.
How does Vertical Agriculture work?
Vertical Agriculture can address many agricultural challenges by producing more food on less land efficiently. But how does it function?
There are various models of vertical farming, ranging from small patio gardens to large warehouses with stacked trays and community-feeding greenhouses like ours. At Viemose DGS, we use our innovative Moving Gutter Systems in vertical structures with stacked plant spots for our Vertical Farming System.
Our design ensures crops have access to natural sunlight, reducing land, water, and energy waste. Additionally, our advanced efficient system allows comprehensive farm control, optimizing crop cycles and yield production to meet demand.
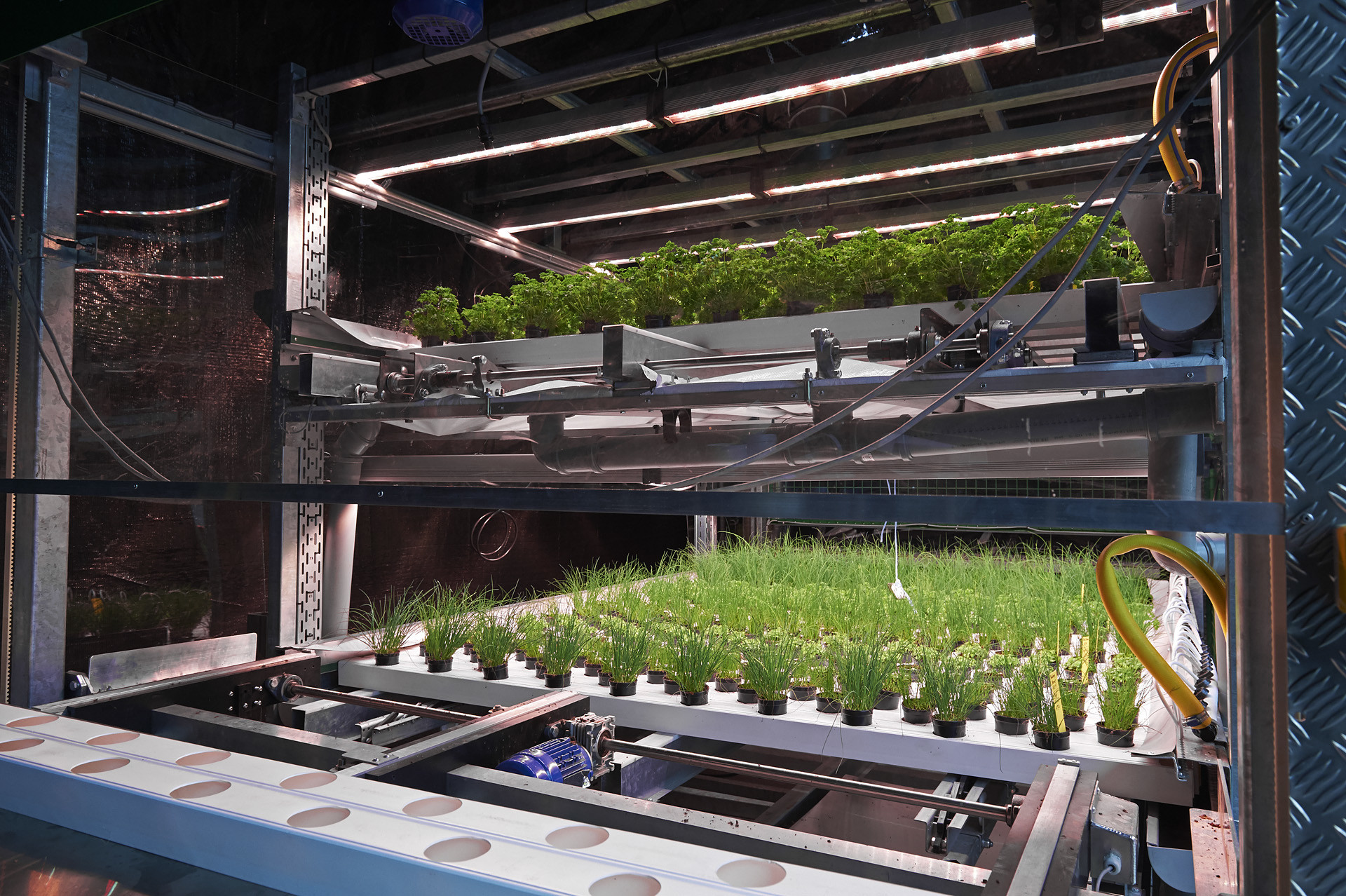

Benefits of Vertical Agriculture
As we look for efficient solutions to meet the growing demand for food, Vertical Agriculture emerges as a transformative approach with numerous advantages. By rethinking traditional farming practices and harnessing innovative technologies, vertical agriculture offers a path to more efficient, resilient, and conscious food production.
Below, we explore the various benefits of Vertical Farming and how it can address some of the most pressing challenges in modern agriculture.
Efficient Use of Space
Vertical Agriculture maximizes the use of space by allowing crops to grow in vertically stacked layers. This approach is especially beneficial in urban areas where land is scarce and expensive.
By utilizing vertical surfaces, farms can produce more food in less space, making it possible to grow crops in places that would otherwise be unsuitable for traditional agriculture.
Year-Round Crop Production
One of the key advantages of Vertical Agriculture is the ability to control the growing environment. With precise regulation of temperature, light, water, and humidity, crops can be grown year-round, regardless of external weather conditions. This leads to a more consistent and reliable food supply, reducing the risk of crop failures due to adverse weather.
Reduced Water Usage
Vertical Agriculture often employs hydroponic or aeroponic systems, which use significantly less water than traditional soil-based farming. These systems recycle water, ensuring that crops receive the necessary hydration without the excessive waste associated with conventional irrigation methods. This makes Vertical Farming a more efficient option, especially in areas facing water scarcity.
Lower Environmental Impact
Traditional agriculture is a leading cause of deforestation, soil degradation, and greenhouse gas emissions. Vertical Agriculture mitigates these issues by reducing the need for large tracts of arable land and minimizing soil disturbance.
Additionally, by locating farms closer to urban centers, Vertical Farming cuts down on transportation emissions and reduces the carbon footprint of food production.
Enhanced Food Security
As the global population grows, ensuring food security becomes increasingly important. Vertical Agriculture can contribute to food security by producing high yields in small areas, making it easier to feed growing populations.
By integrating vertical farms into urban environments, communities can have direct access to fresh, locally-grown produce, reducing dependence on long supply chains and enhancing resilience against food shortages.
Improved Crop Quality
With controlled environments, Vertical Agriculture can produce higher-quality crops with better flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
The precise management of growing conditions reduces the risk of pests and diseases, often eliminating the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides. This results in healthier, cleaner produce for consumers.
Innovation and Technological Advancements
Vertical Agriculture is at the forefront of agricultural innovation, incorporating cutting-edge technology such as automated systems, artificial intelligence, and advanced sensors.
These technologies enhance efficiency and productivity, making Vertical Farming a continually evolving field that adapts to meet future agricultural challenges.
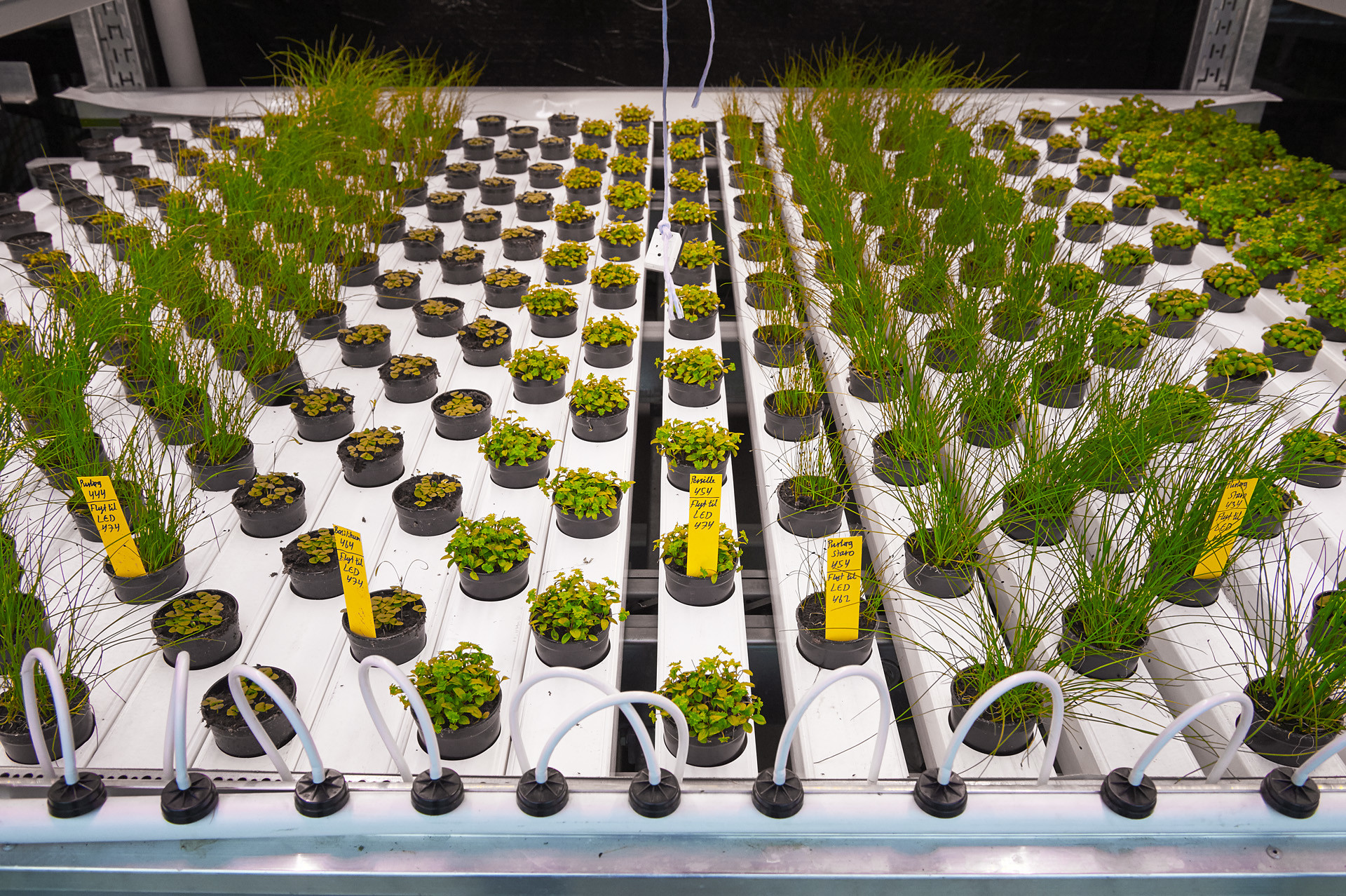

What are the key Considerations concerning Vertical Agriculture?
While Vertical Agriculture holds immense promise for efficient food production, it comes with a unique set of challenges and considerations. Understanding these factors is crucial for anyone looking to invest in or develop a Vertical Farming operation.
From financial investments and energy demands to regulatory issues and market dynamics, several key aspects must be addressed to ensure the success and sustainability of Vertical Agriculture.
In this section, we explore the essential considerations that can influence the viability and impact of Vertical Farming.
Initial Investment and Operating Costs
One of the primary considerations when implementing Vertical Agriculture is the significant initial investment required for setting up the infrastructure. This includes the cost of buildings, lighting systems, climate control, and hydroponic or aeroponic systems.
Additionally, ongoing operating costs can be high due to the need for energy to maintain optimal growing conditions, making economic feasibility a critical factor.
Energy Consumption
Vertical Agriculture relies heavily on artificial lighting and climate control systems, leading to high energy consumption. Ensuring that these systems are energy-efficient and exploring renewable energy sources are essential steps to minimize the environmental impact and reduce operating costs. Balancing the benefits of year-round production with the energy requirements is a key challenge.
Technical Expertise
Successful Vertical Agriculture requires specialized knowledge and skills in areas such as horticulture, engineering, and environmental control.
Growers and operators need to be trained to manage and maintain the sophisticated systems used in Vertical Farming. Access to technical expertise is crucial to ensure the efficiency and productivity of vertical farms.
Crop Selection
Not all crops are suitable for Vertical Farming. High-value crops such as leafy greens, herbs, and certain fruits are commonly grown because they have shorter growth cycles and higher market prices.
Careful consideration must be given to crop selection based on economic viability and market demand. Experimentation with different crops can also help diversify production and increase profitability.
Market Access and Distribution
Vertical farms, often located in urban areas, need effective strategies for accessing markets and distributing their produce. Establishing partnerships with local retailers, restaurants, and consumers can help ensure a steady demand for the produce. Efficient logistics and supply chain management are essential to minimize costs and deliver fresh products to consumers.
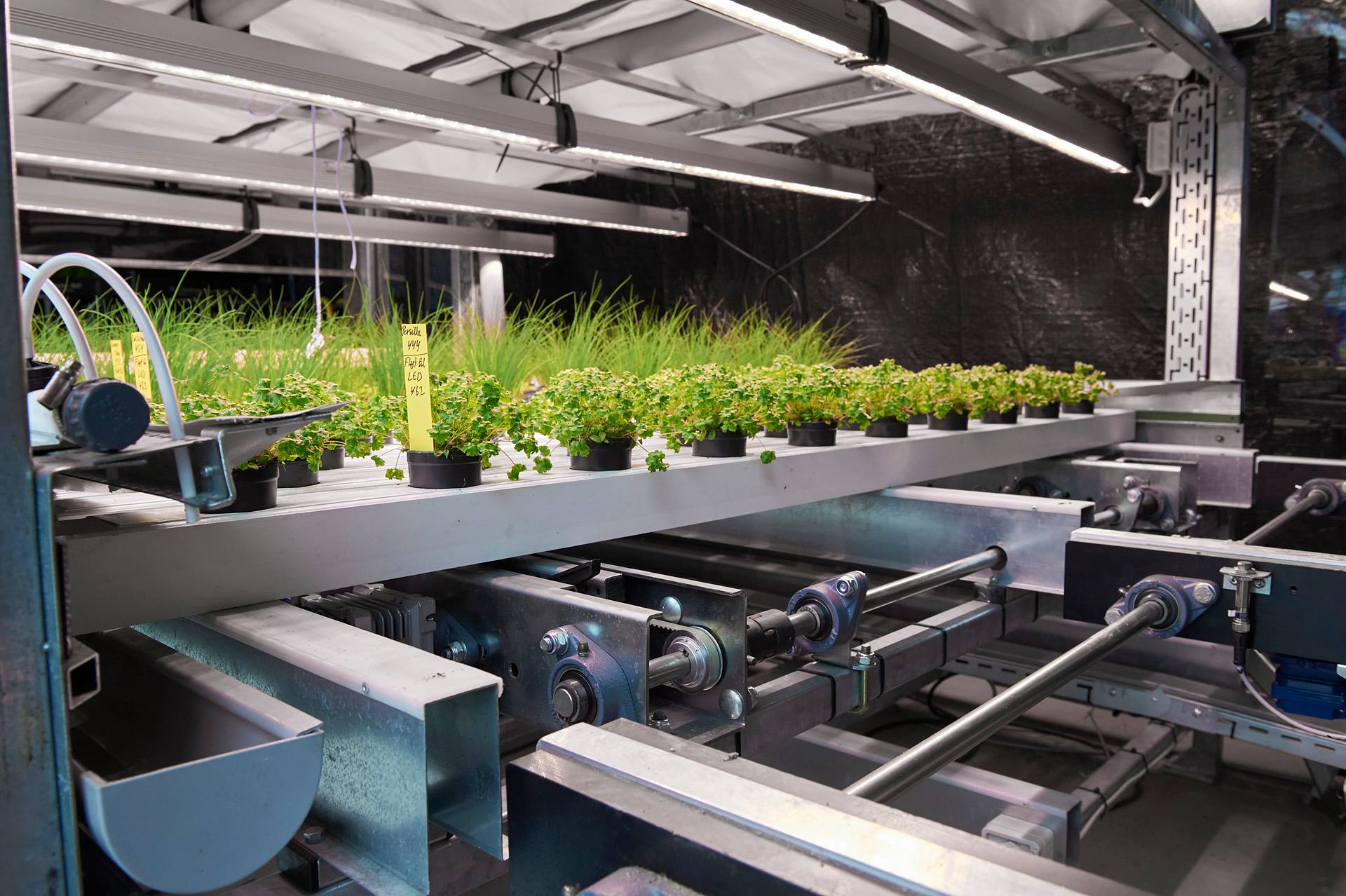

The Future of Vertical Agriculture
Vertical Agriculture represents a significant advancement in the way we approach food production, offering an efficient solution to many of the challenges facing traditional farming. By utilizing vertical space, controlling environmental conditions, and employing innovative technologies, vertical farms can produce high yields in small areas, reduce water usage, and minimize environmental impact.
However, embracing Vertical Agriculture comes with its own set of challenges. High initial investments, energy consumption, and the need for technical expertise are all critical factors that must be carefully managed.
Successful Vertical Farming requires strategic planning, effective market access, and efficient practices to balance productivity with environmental and economic viability.
Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of Vertical Agriculture are compelling. It offers a transformative path forward for agriculture. As we continue to innovate and refine our systems, Vertical Agriculture stands poised to play a crucial role in the future of sustainable agriculture, ensuring that we can feed future generations while protecting our planet.
Viemose DGS at the forefront of Vertical Agriculture
Viemose DGS is at the forefront of addressing future agricultural challenges through the innovative use of Vertical Farming.
By leveraging advanced technologies and efficient practices, our company is transforming the way food is produced, aiming to meet the growing demands of a rising global population while minimizing environmental impact.